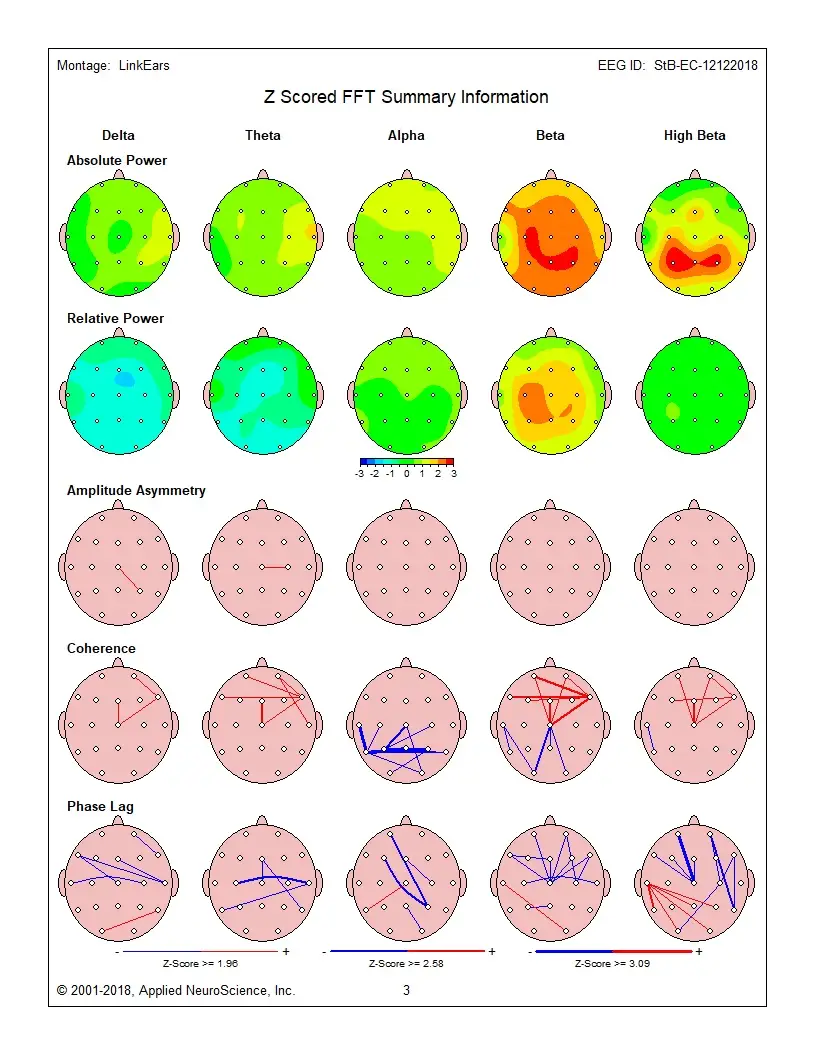
qeeg
qeeg is a specialized approach in our brain training toolkit. Peak Brain Institute applies qeeg as part of comprehensive, QEEG-guided protocols tailored to each client's brain patterns and goals. Explore our 3 articles covering this topic.
3 itemsGet Started →
Blog Articles



Related Research Collections
Related Topics
Ready to Optimize Your Brain?
Schedule a free consultation to discuss qeeg and how neurofeedback training can help
Or call us directly at 855-88-BRAIN
View Programs & Pricing →